To successfully integrate agile methods into organizational structures, many companies opt for the Scrum framework. One of the decisive reasons: Scrum enables teams to work not only sequentially, but simultaneously with each other. In practice, this enables them to coordinate projects better and complete tasks more efficiently.
But what does that mean in numbers? To better understand how Scrum works, I’ll take a detailed look at over 20 Scrum statistics. These show how and why organizations implement Scrum and what challenges they face in doing so. I will also explain which 3 steps are especially important to successfully implement Scrum in a company. To make this easy to understand, I have turned almost all data and numbers into concise statistics, charts, and tables. Let's start with the big overview of Scrum statistics 2023.
Scrum Adoption Statistics: How popular is Scrum?
The Scrum Adoption Statistics 2023 show: Scrum is the most popular agile framework. It is used by companies both as a single agile methodology and as a hybrid methodology.
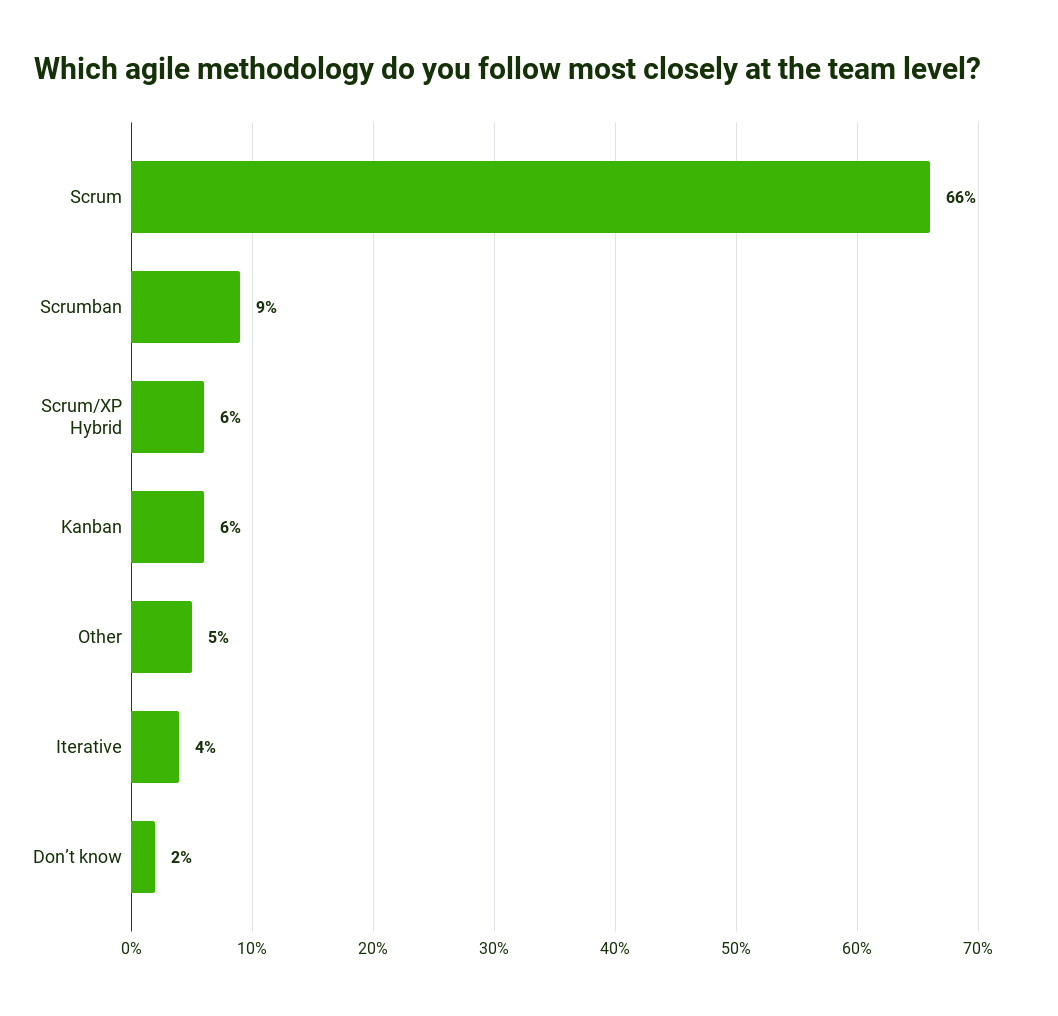
Which agile methodology do companies use?
Source for Scrum stats: 16th State of Agile Report 2022 | Resource Center | Digital.ai
The figures show: 81 percent of agile teams use a variant or hybrid variant of Scrum. It is therefore no wonder that 78 percent of Scrum users would recommend the methodology to colleagues. (study "State of Scrum 2017-2018").
Another study comes to similar conclusions for Scrum Usage statistics:
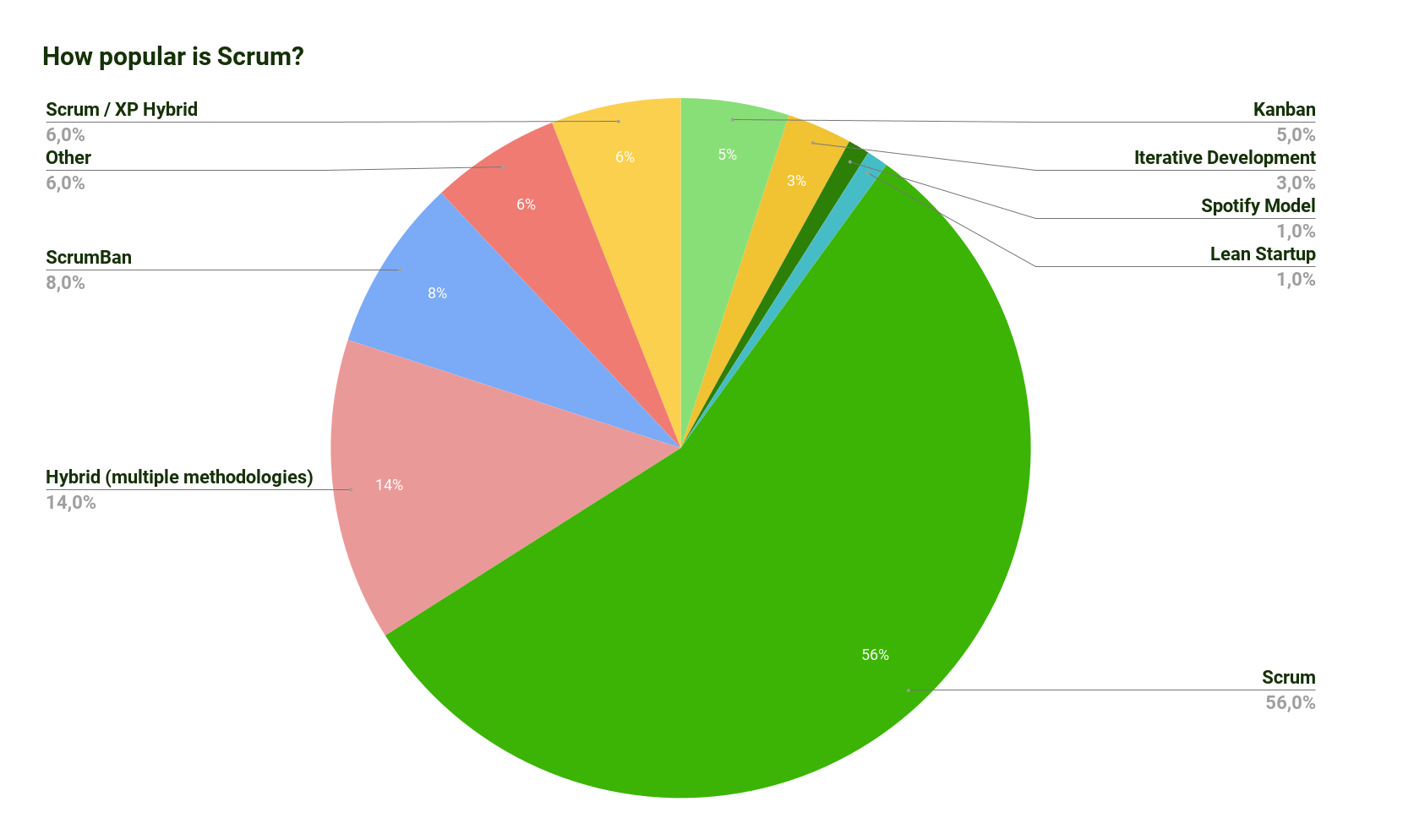
Source for Scrum stats: Latest Reports on the Most Popular Agile Methodologies | Adeva (adevait.com)
Scrum Usage Statistics: How teams benefit from Scrum
Scrum is the most popular methodology for integrating the agile way of working into teams. How do teams benefit from it?
Better quality: Better quality: teams that work fully with Scrum and therefore estimate the workload for their tasks have a 250 percent higher work quality than teams without estimates (study "The Impact of Agile. Quantified.). This is because they can significantly reduce their defect density. For example, teams without estimates have more than 20 errors on average, while Scrum teams make fewer than 10 (overview of 16 Scrum stats).
Better productivity: Better productivity: teams report that they are 3 to 4 times more productive. The best Scrum teams are even up to 8 times more productive (book "SCRUM: The art of doing twice the work in half the time").
Better working life: 85 percent of all teams say their work life has improved because of Scrum ("State of Scrum 2017-2018").
Scrum stats: 6 key challenges when implementing Scrum
With these benefits, it's quickly clear that almost every organization can benefit from Scrum. So why aren't all companies embracing it? The reason is quite simple: there are numerous hurdles on the way towards successful Scrum deployment. What are the challenges that companies face?
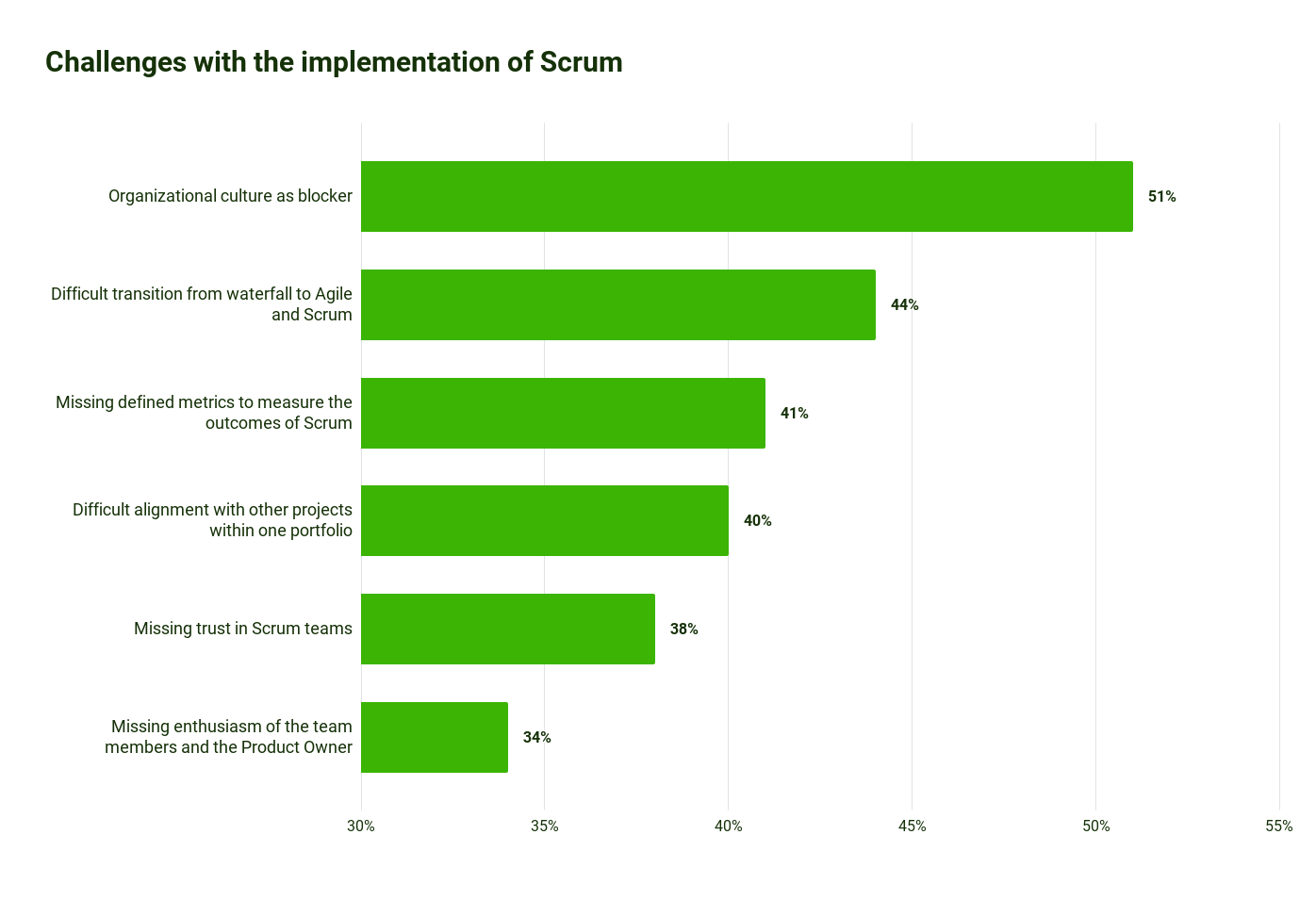
Source for Scrum stats: Latest Reports on the Most Popular Agile Methodologies | Adeva (adevait.com)
Scrum Statistics: What helps companies adopt Scrum?
How can companies ensure they make the transition to Scrum successfully? What should they look for when integrating Scrum into teams? Our experience has shown that 3 pillars are particularly important:
Pillar 1: Introduce the 3 most important Scrum events
Scrum events are an essential part of the framework to anchor its structure and processes in an organization. As a first step, organizations should therefore introduce the 3 critical Scrum events:
1) Sprint Planning
Sprint planning is the meeting at the start of a sprint where teams break down high-level descriptions into detailed tasks. This helps them make a detailed estimate of the amount of work they need to complete during the sprint. 86 percent of all Scrum teams use sprint planning meetings to plan typically 2 week cycles ("State of Scrum 2017-2018").
2) Daily Scrum
Daily Scrum describes a daily stand-up meeting, lasting a maximum of 15 minutes, in which team members discuss their work progress and hurdles. The basic idea is to increase communication within the team. 87 percent of all Scrum teams use Daily Scrum ("State of Scrum 2017-2018").
3) Retrospectives
Retrospectives are perhaps the most important agile event that works well to introduce the agile mindset to teams: at the end of the 2-week sprint, the Scrum team reflects on what went well and what went poorly. Retrospectives are thus the core event for a basic idea of agile ways of working: continuous improvement.
"If you adopt only one agile practice, let it be retrospectives. Everything else will follow."
Agile Guide Woody Zuill
Scrum Stats: Why do organizations need retrospectives?
90 percent of all people consider themselves to be above average drivers (Svenson, 1981). Is that statistically possible? It is more likely that people overestimate themselves. This can also be applied to the world of work. Often, managers in particular think they are more competent than they are. As a result, they stop reflecting on the quality of their work. They become resistant to change.
How can managers – and all other employees – prevent themselves from becoming resistant to change? The fact that people can fundamentally change is genetically ingrained in us. Only 50 percent of our personality is genetically predisposed (Guo, 2005). So, we have 50 percent in our own hands.
To avoid becoming resistant to change, we must regularly reflect on our behavior. Retrospectives can be very helpful in this regard. Employees use retros to review key pillars of their progress, success, and failure. Retrospectives reveal not only productivity and work quality, but also employee satisfaction. As a result, team members regularly evaluate their work. This prevents them from making the same mistakes over and over again. What's more: it ensures that they approach their tasks with a better sense of progress and efficiency.
Agile Scrum Statistics: How can organizations introduce retrospectives?
At best, retrospectives are adopted voluntarily by teams after trying them out selectively for a few sprints. To give you a sense of how retros are designed, here are some statistics on them:
Duration of retrospectives
Retrospectives should neither be too long, so that employees don't get bored or exhausted, nor too short, so that the reflection has substance. What does this mean in practice?
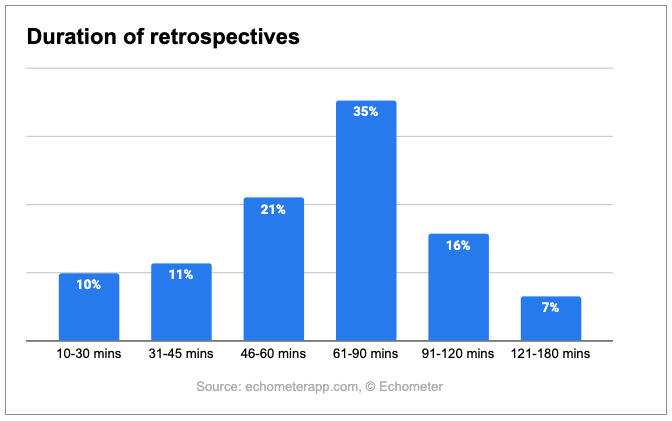
The average retrospective lasts 1 hour and 11 minutes. Only around 7% of retrospectives last longer than 2 hours. Short retrospectives between 10 and 45 minutes still account for 21%. This is what our analysis of 30,000 retros with Echometer found out (Echometer analysis of 30,000 retros).
If the average of all retros is 1 hour and 11 minutes, does that also mean that this is the best length? We can answer that with a "no" – at least from the perspective of retros participants.
Team members are particularly satisfied when retros last 31-45 minutes. This is shown by the so-called ROTI score. The ROTI score is the average rating of the time invested in a retrospective. With a score of 0 participants indicate that the time was poorly invested, and with a score of 10, they indicate just the opposite. For retros of 31-45 minutes, the ROTI score was highest at 8.5 points. Retros with a length of 46-60 minutes follow directly behind. They come to a ROTI score of 8.47 points.
Number of participants of retrospectives
How many team members should participate in a retrospective to make it particularly efficient? For this I have these Agile Scrum statistics:
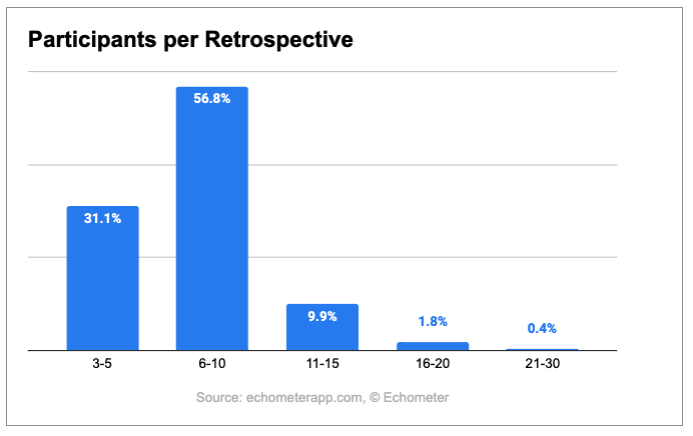
This translates into: Just under 90 percent of retrospectives have 10 or fewer participants. Again, let's take a look at the ROTI score: At what number of participants were teams most satisfied with the retrospective? With a score of 8.64 points, retrospectives with 3-5 participants have the best rating.
Frequency of retrospectives
How often should teams conduct retrospectives?
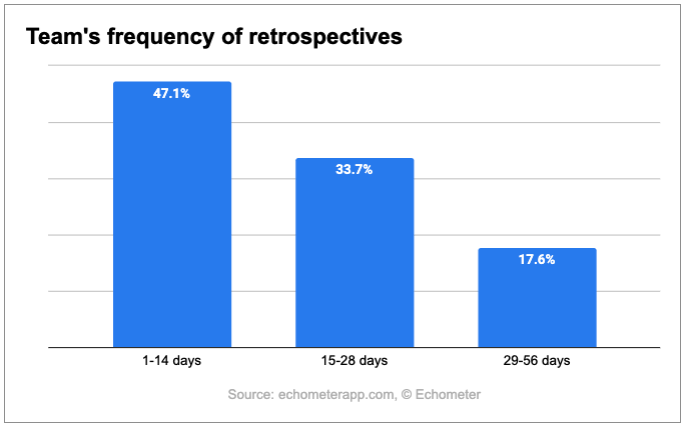
Most teams conduct a retrospective every 14 days or more often. This time, the statistics coincide with the ROTI score. At 8.61 points, this frequency ensures that employees see their time as particularly well invested.
How do teams benefit from retrospectives?
Retrospectives ensure that employees reflect on their work. How do they benefit from this?
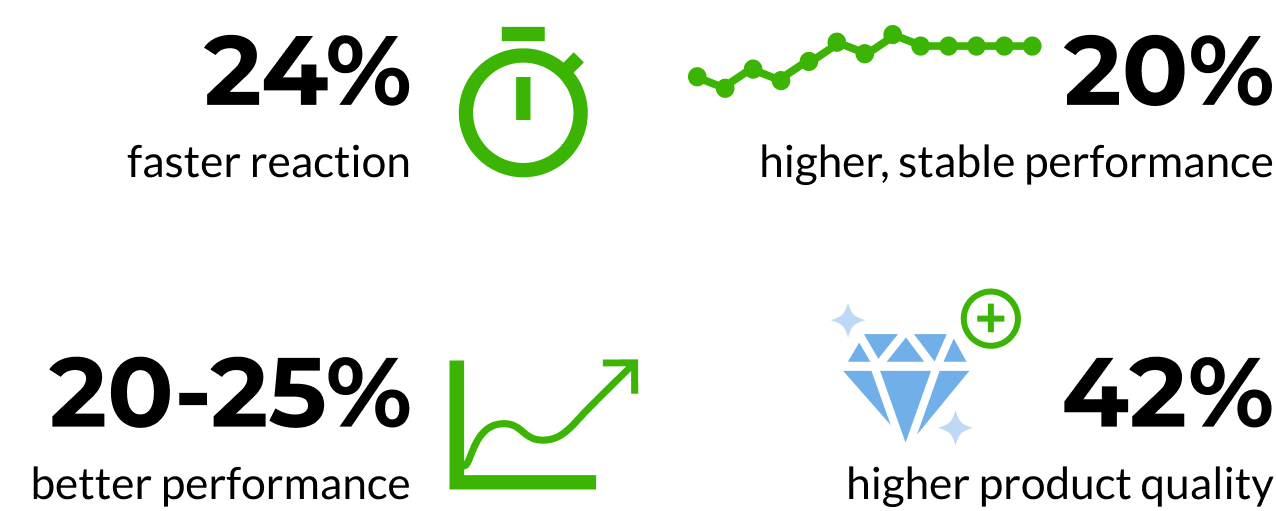
Source for Scrum statistics: Study by Tannenbaum & Cerasoli / Study from Broadcom Software
By the way: By the way, another study even came up with a 100% better performance when teams rely on a very specific type of retrospective. If you're interested, take a look at our eBook which shows you 12 steps to better agile teams. It's entirely free (eBook Mindset Change & Team Flow Workshops).
With these numbers in mind, it's not surprising that 81 percent of all Scrum teams hold a retrospective after each sprint ("State of Scrum 2017-2018").
Pillar 2: Hire a Scrum Master
To run projects with Scrum and hold Scrum events, your organization needs a Scrum Master or at least a similar role (More about the role of the Scrum Master). The Scrum Master is one of the servant leaders in agile frameworks. He or she is responsible for leading a project through all hurdles to a successful conclusion.
To be up to these tasks, Scrum Masters often have an education from the IT field. However, this does not have to be the case. They can also come from other professional fields:
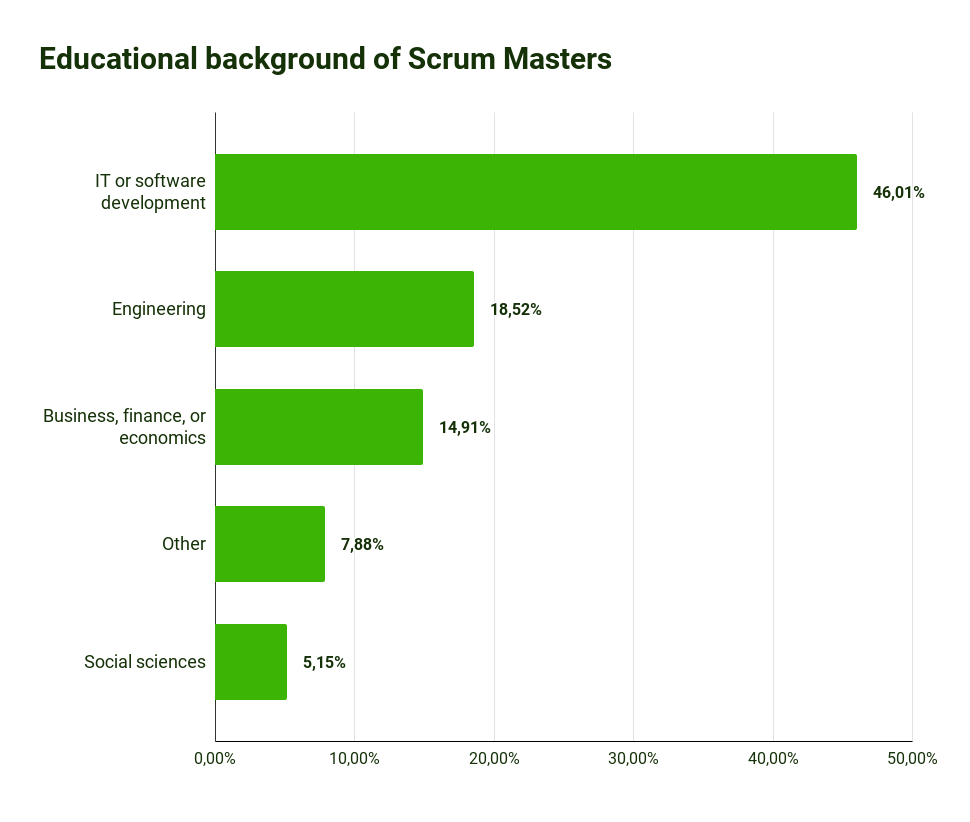
Source for Scrum Master statistics: 2019 Scrum Master Trends Report | Scrum.org
To take on the role of a Scrum Master, professionals typically have at least one certification in the agile methodology:
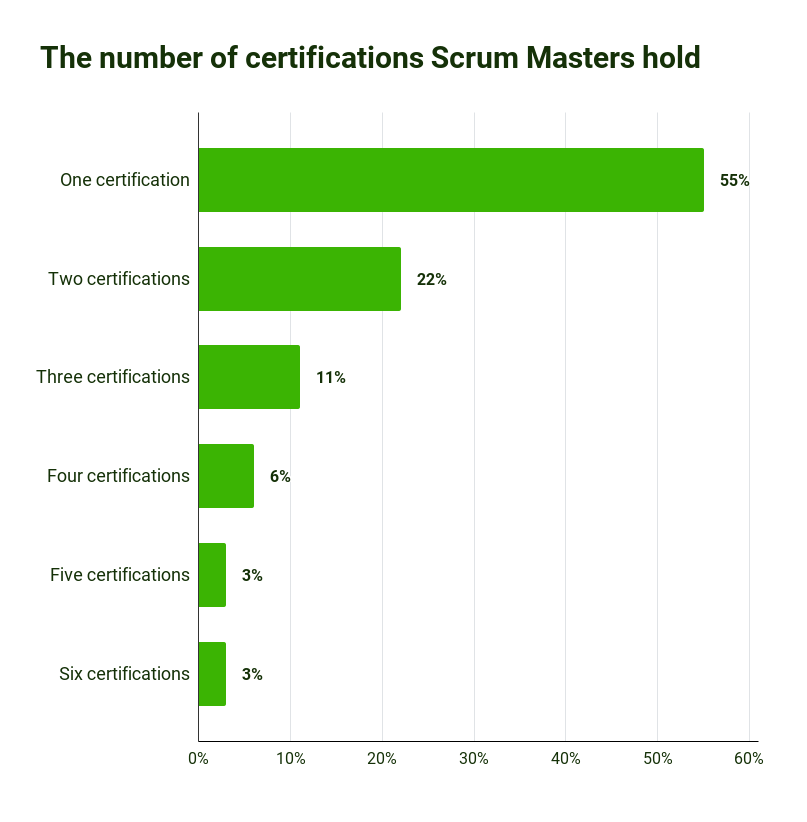
Source for Scrum Master statistics: 2019 Scrum Master Trends Report | Scrum.org
Scrum Stats: What is the cost of a Scrum Master?
One Scrum Master is good, several are better (assuming they understand their job). Depending on the size and number of teams in the company, you can't get by with one Scrum Master. To help you know how much budget you need to hire a Scrum Master, let's take a look at the salary:
Average Scrum Master Salary after graduation
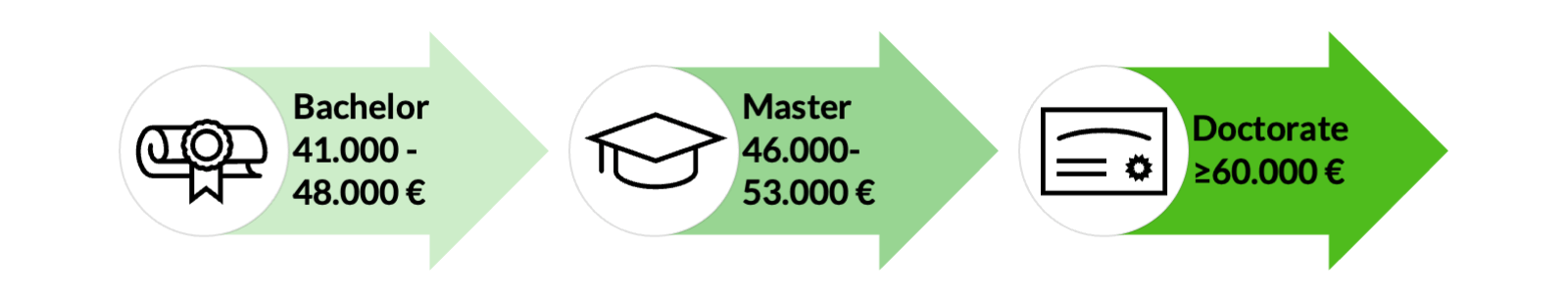
Source Scrum Master statistics: What does a Scrum Master earn? | get in IT (get-in-it.de)
Average starting salary for Scrum Masters by company size
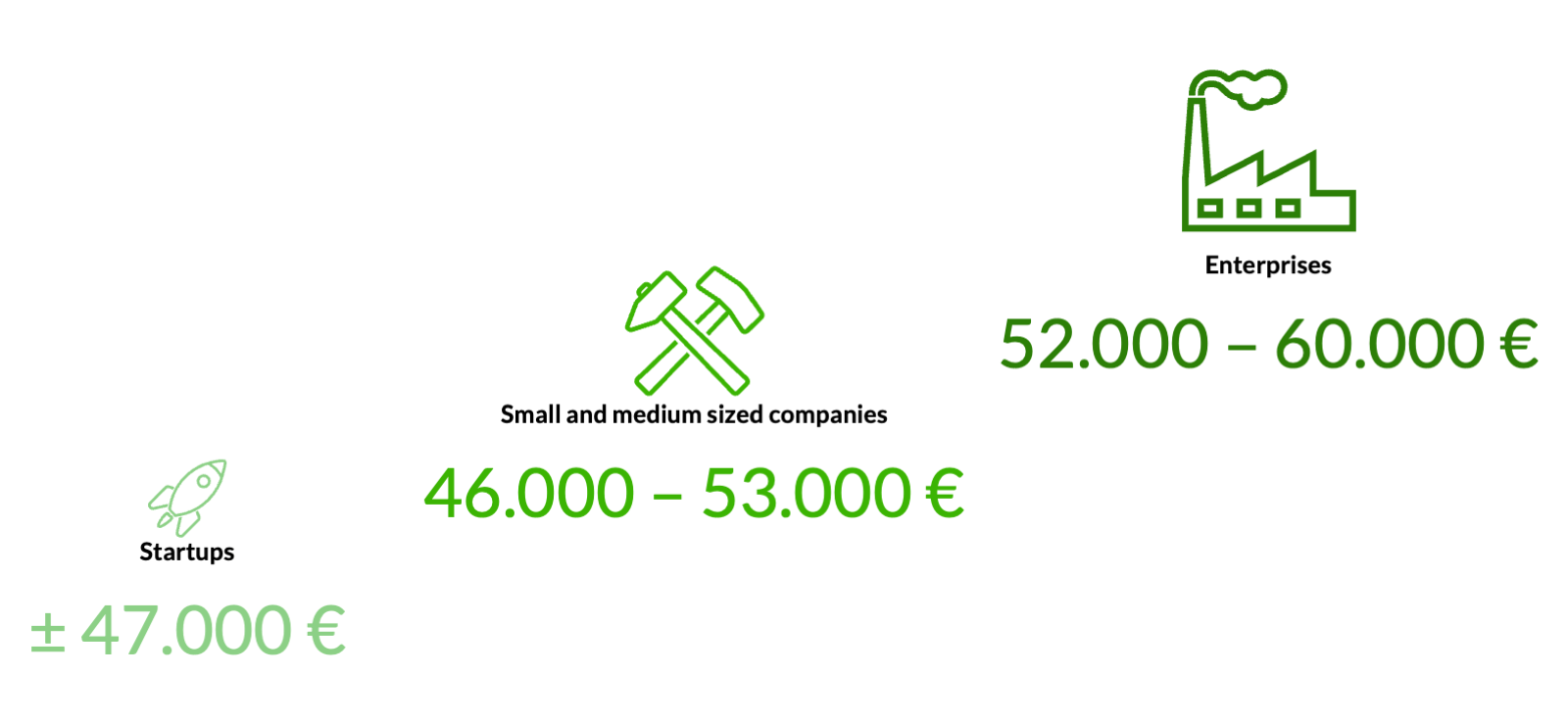
Source Scrum Master statistics: What does a Scrum Master earn? | get in IT (get-in-it.de)
Salary for Scrum Master: Average starting salary for Scrum Masters by Industry
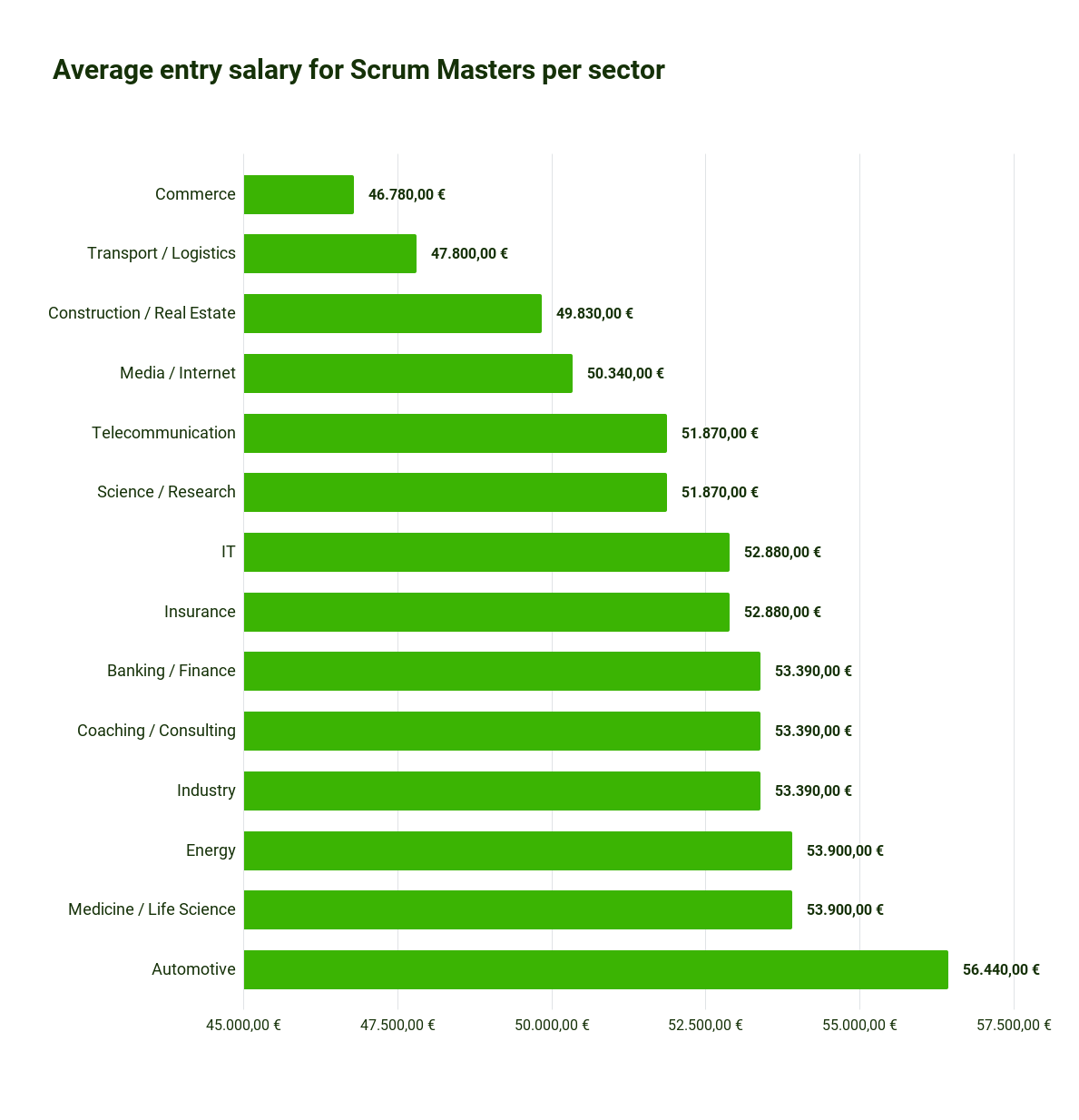
Source Scrum Master statistics: What does a Scrum Master earn? | get in IT (get-in-it.de)
Salary for Scrum Master in Germany by work experience
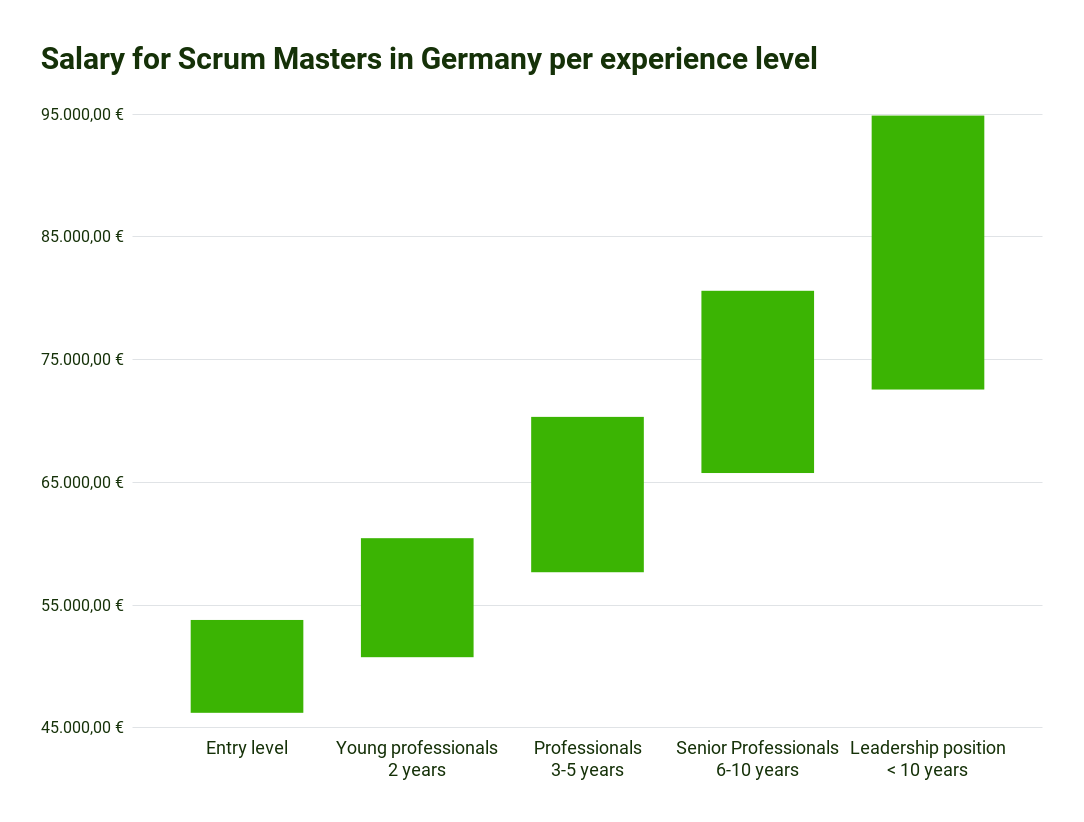
Source Scrum Master statistics: What does a Scrum Master earn? | get in IT (get-in-it.de)
Salary for Scrum Master in the USA by work experience
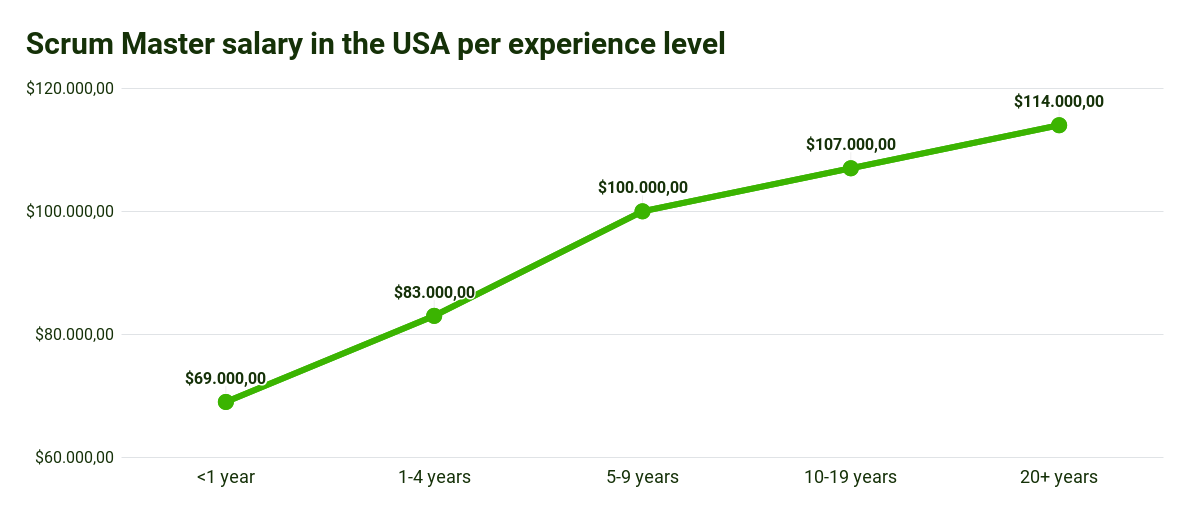
Source for Scrum Master statistics: Scrum Master Salary in USA? 2022 Guide with 10+ High-Paying Companies (hiration.com)
Pillar 3: Deciding on a scaling method
If you are just starting to implement Scrum in your organization, then this third pillar is less important to you for now. However, if your organization is already working agile in some areas and you want to implement Scrum on all levels, then you need an agile framework. Only with a framework you can scale Scrum without it going haywire. For this purpose, the framework provides you with a series of organizational and workflow patterns that you can use to design work areas in an agile manner.
Which frameworks are particularly common for this?
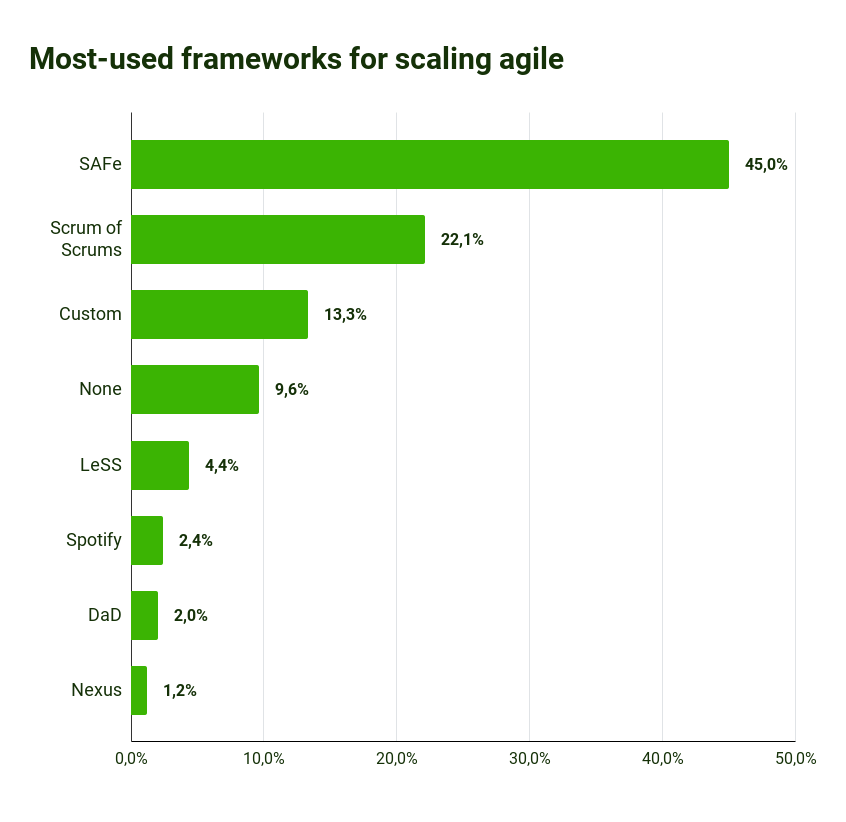
Source Scrum Adoption Statistics: Latest Reports on the Most Popular Agile Methodologies | Adeva (adevait.com)
The Agile Report 2022 came to a similar conclusion:
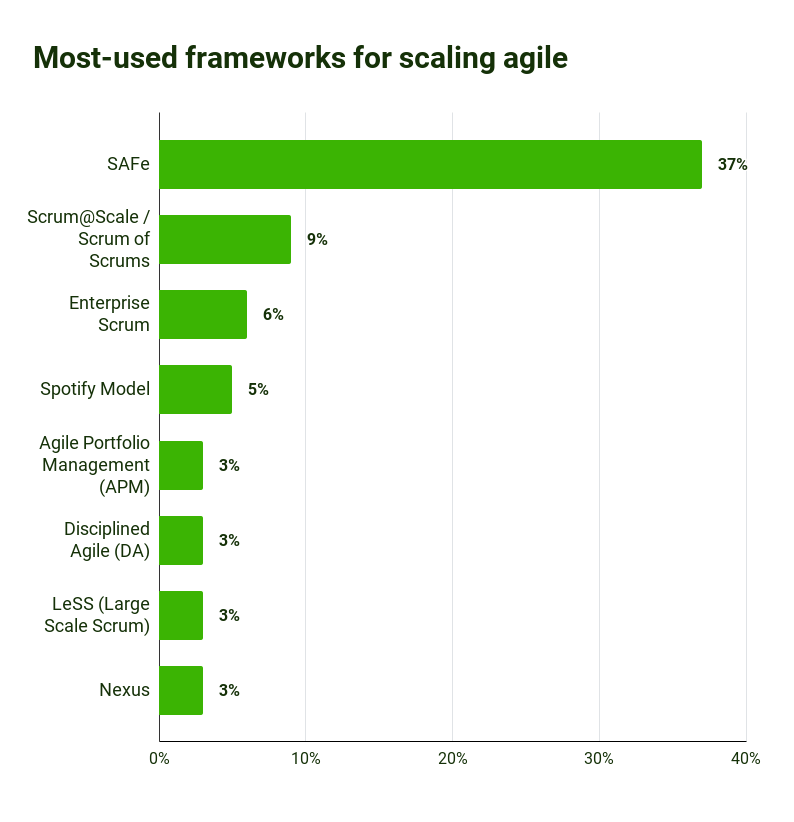
Source Scrum Statistics 2023: 16th State of Agile Report | Resource Center | Digital.ai
Conclusion
Scrum enables companies to develop products faster and better. However, before they can work flawlessly and efficiently with the agile framework, they need to introduce it to teams. This is most successful when organizations start with the 3 most important Scrum events: Sprint Planning, Daily Sprint and Retrospectives.
Even though Scrum is common and effective, it doesn't mean that it is perfect for every context. There are scenarios where waterfall methods also have a justification (Agile vs. waterfall method). Basically, it is undoubtedly worth talking to an expert in the field before making a decision. At the beginning there must be these questions: What is our problem? Why do we want change? Then you can ask the question: which tool or framework can best solve this problem?
Finally, a hint: When it comes to agile retrospectives, our Echometer tool can help you (Echometer tool). With this tool, you can conduct retrospectives that sustainably and measurably develop your company. You can use them not only to reflect on the work you've done, but also to gradually shape the mindset and culture in your organization in an agile way – and even make it measurable. To help you know how to leverage retrospectives in your organization, take a look at our free eBook (eBook 20+ Facilitation Tips for great retrospectives). Because as you may have noticed above: retros are almost always a useful start to successful agile transformations.
Most Agile Coaches and Scrum Masters run in circles...
...fixing superficial symptoms. Time to use psychology to foster sustainable mindset change.